Heavy metal contamination of soil is long-term ecological problem
INTRODUCTION:
The quality of human life depends on the chemical composition of the environment, including food, water, and many other factors necessary for life. The development of human society, however, has brought substantial increases in ecological problems and contamination of the environment [1]. Some parts of the environment (e.g. atmosphere and hydrosphere) are able to partially remove the contaminants or to disperse them over wide areas and eliminate their potentially ecotoxic effects. The pedosphere, however, cannot, and important “hot-spots” with extremely high levels of a variety of pollutants have developed concurrently with human society in recent decades [2]. Soil is one of the most important factors for terrestrial life through the production of food, so its degradation could reduce the diversity or abundance of various valuable organisms necessary for maintaining balanced ecological functions [3]. Understanding the impact of pollution on important soil processes, where soil organisms play key roles, requires observing not only the quantity of the pollutants in a system, but also their qualitative effects and ability to change the environmental conditions for soil biota [4]. Various approaches using different soil communities were thus developed for biomonitoring potentially endangered ecosystems. The wide variety of communities, either directly in the soil or above it, tightly linked to soil processes makes the selection of an appropriate bioindicator challenging. Soil mesofauna, composed of various invertebrate communities, are the most suitable [5]. Soil invertebrate communities are able to buffer short-term resource shortages without significant losses in abundance or diversity [6], but they also have relatively rapid and identifiable reactions to contamination, because they are integrators of the physical, chemical, and biological properties related to their food resources [5]. Within the mesofauna, soil nematodes [7], springtails [8], and mites [9] have been considered for use as reliable bioindicators. Nematodes may be the most promising candidates for systems of bioindication, because more information on their taxonomy and ecology [10] is available than for other animal groups.
NEMATODES AS BIO INDICATORS
Nematodes are amongst the most abundant multicellular organisms in nearly all soil ecosystems, occupying key positions at most trophic levels in the soil food web [11]. They are involved in organic matter mineralisation, plant growth, and crop productivity by their regulation of detritivore populations and thus contribute to the stability of the food web [12, 13, 14]. Their life cycles have been widely studied, partly because some taxa are pests [15]. The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is a key model for genetic studies, which could significantly improve the bioindicating potential of nematodes on molecular and gene-expression levels. The introduction of the maturity index by [7], one of the best-known indicators of soil health [15], was a crucial breakthrough in nematode bioindication. Nematodes are classified in this system along a coloniser-persister (c-p) continuum and assigned to c-p groups ranging from 1 (colonisers) to 5 (persisters). Similar to the r/K dichotomy, colonisers are characteristic of early successional stages, and persisters are found mainly in more developed and complex ecosystems. The advantage of the c-p system is that nematodes only need to be identified to the generic level, which does not affect the resolution of the indication. Several other derived or new ecological indices have been developed from the maturity index. Ferris et al. [11] provided a framework for determining the enrichment (enrichment index, EI) and structure (structure index, SI) of food webs based on the relative weighted abundance of the functional guilds of nematodes. A matrix of feeding habits, with life history characteristics embodied in the c-p classification, is used to enhance the resolution of nematode analyses and to connect the functional groups with the enrichment and structure of the food web and channels of decomposition.We applied these approaches at two locations, Kovohuty JSC Krompachy and Slovak Magnesite Works JSC Jelšava, with soils contaminated by dust fallout containing high amounts of potential ecotoxic elements. The levels of contamination at these sites have been analytically determined, but little is known about the soil communities and their interactions or about the general health of the soil. The aims of this study were thus to improve our knowledge of the polluted sites and to better understand the biotic processes under environmental pressure and the consequences of industrial pollution for soil food chains.
The specific objectives were
i. To clarify the impact of contamination on the quality of soil abiotic and biotic components.
ii. To evaluate the ability of soil nematode communities to detect ecosystemic disturbances.
iii. To define the suitability of this system of bioindication for the detection of soil degradation.
Material and methods
Study areas
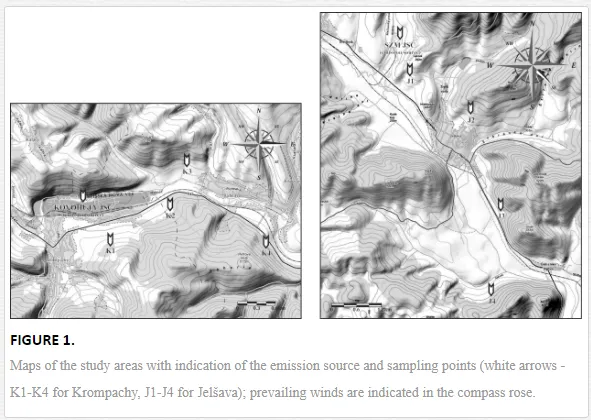
The study was performed in the model towns of Krompachy and Jelšava that have important emission sources, smelters Kovohuty JSC Krompachy and Slovak Magnesite Works Jelšava (SMZ JSC). Krompachy has been known for its processing of iron and copper ore since the 14th century, and copper has been distributed all over Europe. The magnesite industry in Jelšava has flourished since the end of the 19th century. Soil contamination in both areas is caused by the fallout of solid particles containing various elements during the mining and processing of the ores [16]. More than an estimated 1500 tonnes of solid particles yearly containing accessorial elements (Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Ni) from Kovohuty JSC Krompachy, and as many as 165, 000 tonnes of emissions containing magnesium in total from SMZ JSC were emitted to the atmosphere between the 1960s and the 1990s [17].
Sampling and data analysis
Soil samples were collected in April 2010 for Krompachy and in May 2009 for Jelšava at four sampling sites each along transects downwind of the emission sources (Figure 1). Four 1 kg replicates (each consisting of four subsamples) were collected from the surface horizons (0-20 cm) of permanent grasslands at each sampling site by quadrat sampling. Each replicate was stored in a plastic bag at 4 °C until analysed. The soil samples were analysed for geochemical properties and nematode community structure.
GEOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND HEAVY METALS
The soil samples were processed as follows:
1. Soil moisture was measured gravimetrically by drying the replicates to a constant weight at 105 °C [18].
2. Organic matter content (Corg) was determined by titration with K2Cr2O7/H2SO4 [18].
3. NH4+ was determined spectrophotometrically using Nessler reagent [18].
4. NO3– was determined by an ion-selective electrode [18].
5. pH was determined in a solution of CaCl2 [18].
6. The total and mobilisable concentrations of heavy metals (As, Cd, Cu, Cr, Mg, Ni, Pb, and Zn) were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry on an Agilent 7500 C (Agilent Technologies, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The replicate samples were air-dried before analysis in an oven at 30 °C for 48 h or until constant weight, ground, and sifted through a 0.2-mm sieve. Metals were extracted by 2M HNO3 (10 g of soil in 50 mL of HNO3) for 6 h for total content and by 0.05M Na2EDTA neutral solution (5 g of soil in 50 mL of Na2EDTA) for mobilisable content [19].
Steps 1-5 were performed by the Laboratory of the Central and Testing Institute in Agriculture in Košice, Slovakia according to certified methods [18].
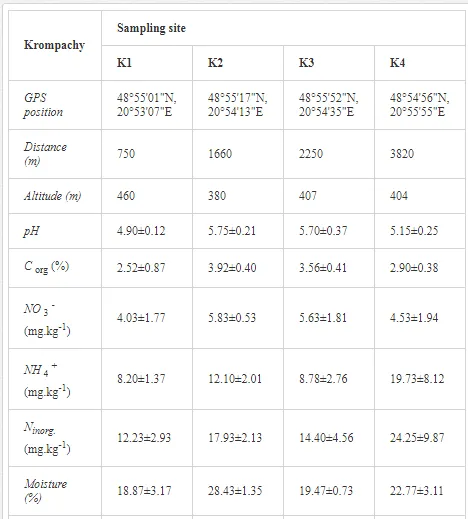
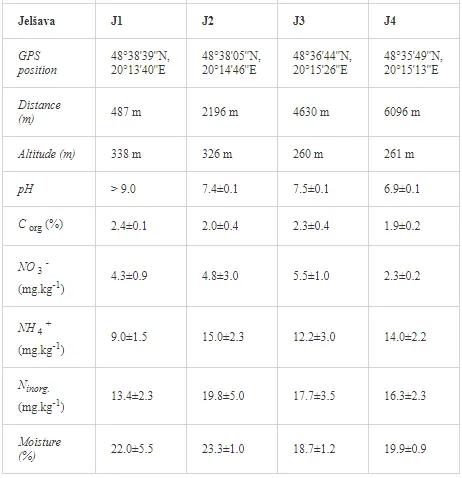
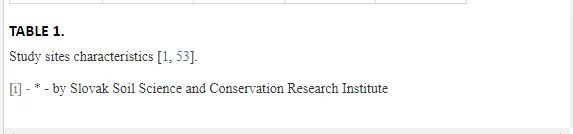
Loamy Cambisols with intense stony skeletons dominated in both areas. Despite some variations in soil properties, the basic characteristics of the soils were similar (Table 1), with soil moistures ca. 20% and inorganic nitrogen contents (Ninorg.) between 10 and 20 mg kg-1. The Krompachy soils were richer in Corg and were more acidic than the Jelšava soils (soil pH >9).
ANALYSIS OF NEMATODE COMMUNITY STRUCTURE
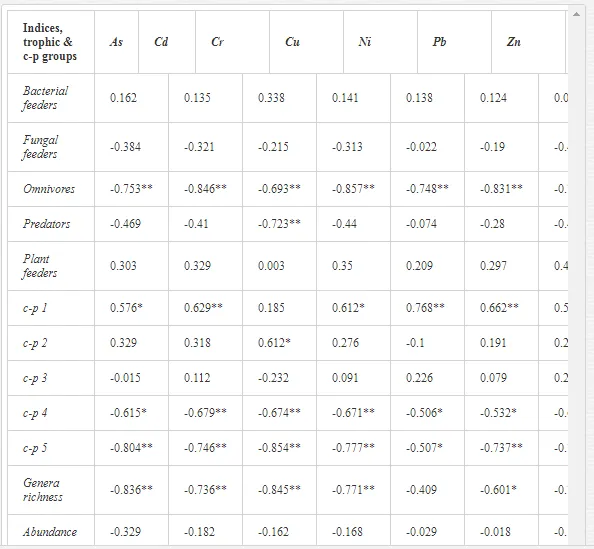
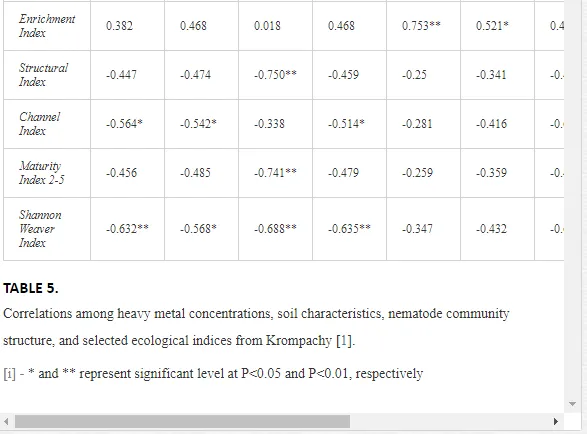
Nematode communities were isolated by extraction from 100 g of each replicate soil sample using a modified Baermann procedure [20]. The extracted nematodes were fixed in Ditlevsen’s solution (formalin/acetic acid/alcohol) [21] and were counted using a microscope. All nematodes in the samples were classified to order, family, and genus. The nematode communities were analysed for (i) total abundance (number of individuals per 100 g of soil), (ii) trophic structure (bacterial feeders; fungal feeders; plant feeders; omnivores; and predators) [22], and (iii) the ecological indices (1) MI2-5 [23] with Nemaplex c-p values, (2) the Shannon-Weaver index (H´) for generic diversity [24], (3) generic richness, expressed as mean number of genera at a site, (4) EI based on the proportion of opportunistic bacterivorous and fungivorous nematodes, (5) SI based on the relative weighted abundance of guilds representing the structure of the food web, and (6) the channel index (CI) [11].


DATA ANALYSIS
Spearman’s nonparametric correlation coefficient (rs) was calculated using STATISTICA v. 9.0 to test the relationships between the characteristics of a nematode community and the concentrations of mobilisable heavy metals at a site [25]. Correlations at P<0.05 and P<0.01 were considered significant. Differences in the mean traits and indices of a community amongst sites were tested by Duncan’s tests. We used a constrained ordination redundancy analysis (RDA) in CANOCO 5 to analyse the ecological distances between sites (nematode community and soil parameters). The significance of an axis was tested by Monte Carlo permutation [25]. The effects of contamination on soil ecosystems can be categorised as direct or indirect. Alterations in the soil communities near Kovohuty JSC Krompachy were likely due to direct toxicity from the high levels of heavy metals in the soil samples. The contamination acted mostly indirectly near SMZ JSC, altering the basic soil properties. We will present and discuss the results from these two areas separately.

Direct toxic effects of industrial emissions – A case study at Kovohuty JSC Krompachy
RESULTS
HEAVY METALS
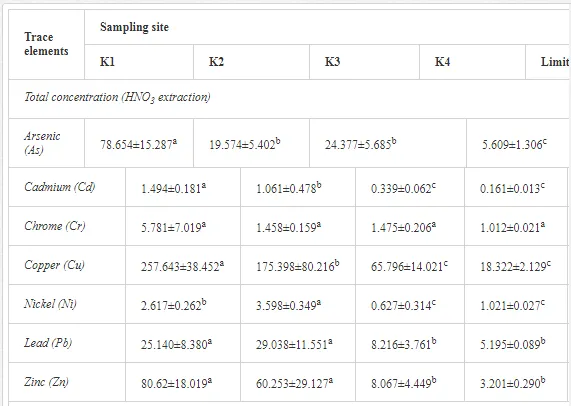
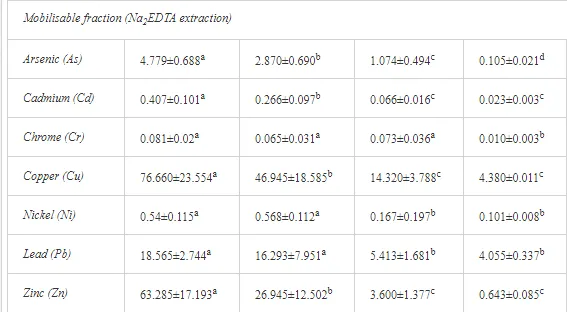
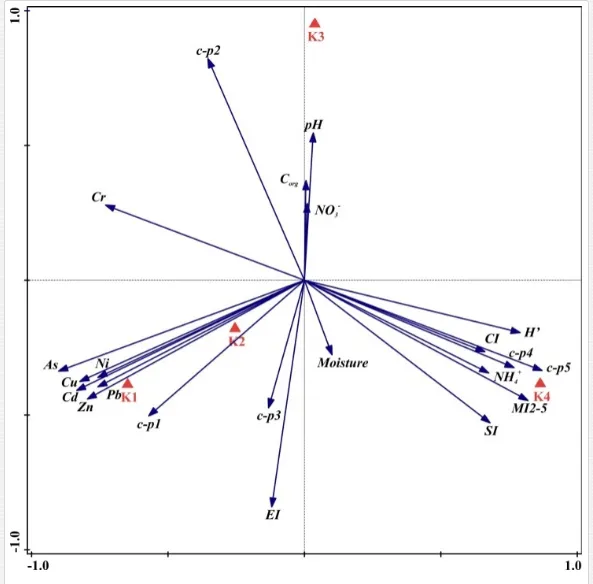
The total heavy metal content (except Pb and Ni) along the Krompachy transect was highest at the K1 site and decreased downwind (Table 2). The patterns of the decreases in concentration, however, varied amongst the metals. As, Cd, and Cu decreased significantly (P<0.05) and relatively continuously towards K4. The concentrations of Ni, Pb, and Zn were relatively high at sites K1 and K2 but were significantly lower at K3 (P<0.05). Cr content did not vary significantly (P>0.05) along the transect. The mobile fractions of all metals had similar decreasing trends (Table 2). As, Cd, Cu, and Zn had high total concentrations, exceeding the limits for uncontaminated soils in Slovakia [26] (Table 2). Corg and pH were likely the most important factors influencing the mobility of the metals, and the RDA (Figure 2) indicated that they were negatively correlated with the concentrations of all heavy metals except Cr.
COMPOSITION OF THE NEMATODE FAUNA: TROPHIC AND C-P GROUPS
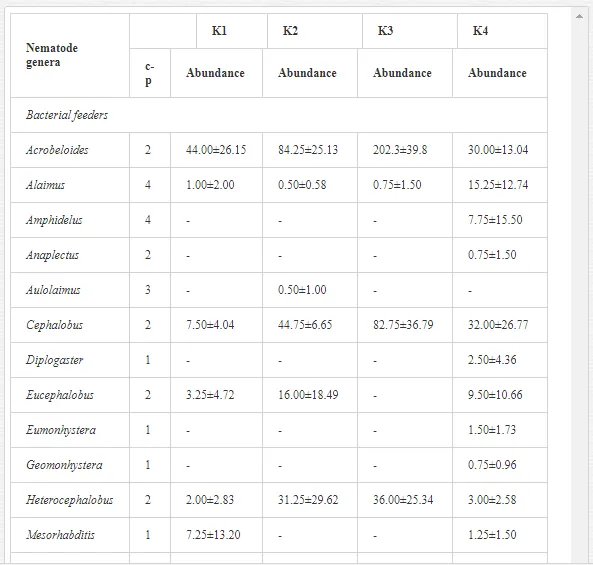
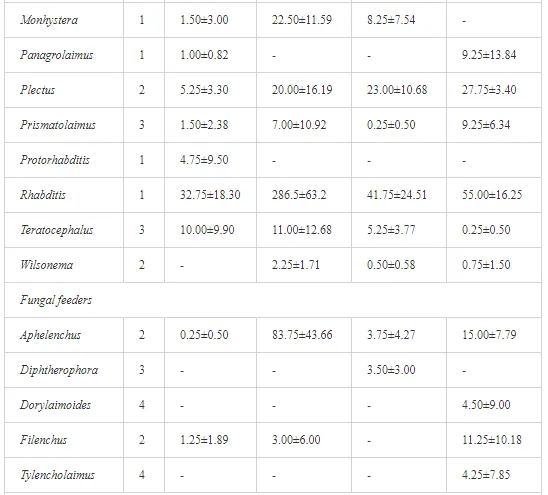
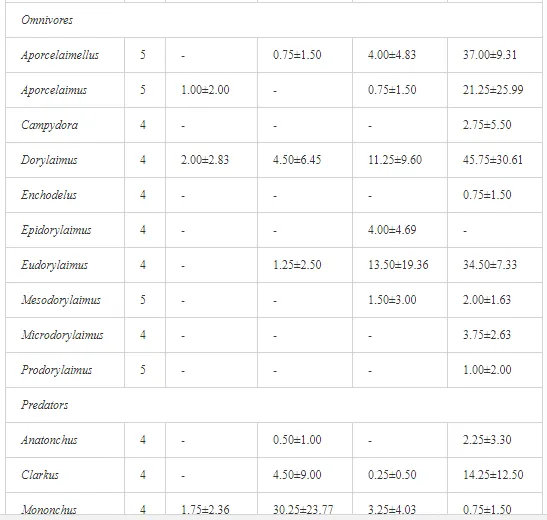
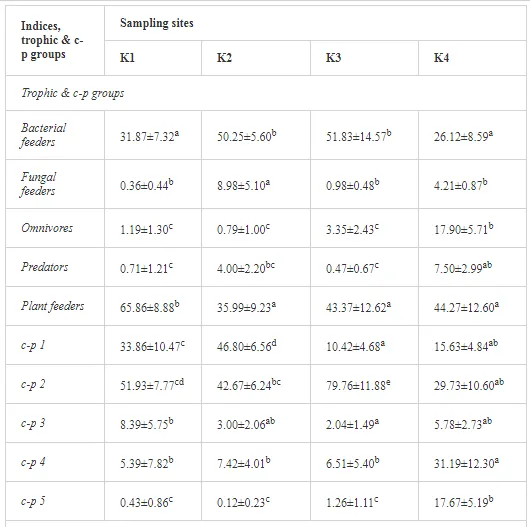
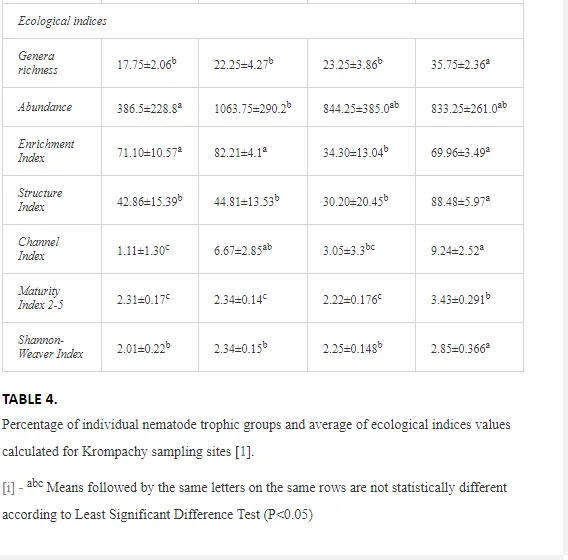
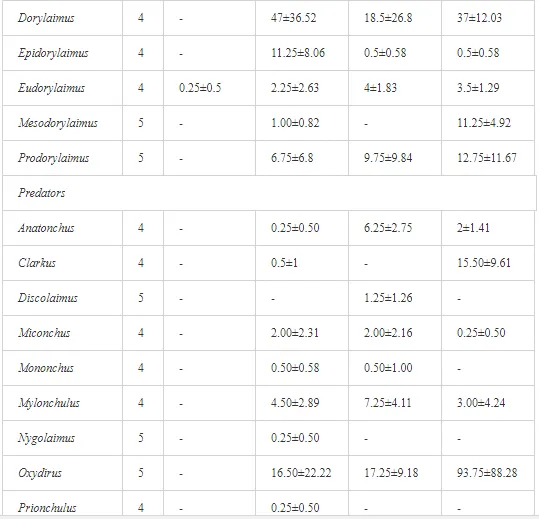
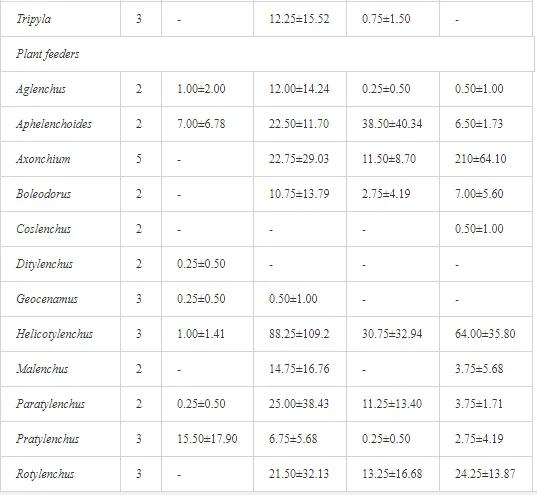
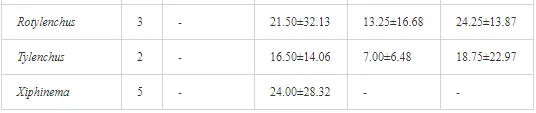
A total of 58 genera were identified, including 20 bacterivores, five fungivores, 10 omnivores, eight predators, and 15 plant feeders (Table 3). The most common genera in the communities were Acrobeloides, Aphelenchoides, Geocenamus, Helicotylenchus, Paratylenchus, Pratylenchus, and Rhabditis (Table 3). The mean number of genera (17.75) in the replicates was lowest near the industrial plant (K1), which also had the lowest mean population density of 386.5 per 100 g of soil (Table 4). Both parameters increased with distance from the plant to 35.75 and 833.25, respectively, at K4. Ninorg. was significantly correlated (P<0.01) with generic richness, and soil pH (P<0.01) and Ninorg. (P<0.05) were significantly correlated with nematode abundance. The industrial complex affected the densities of the trophic groups. The trophic structure differed at each sampling site (Table 4). Plant feeders were the most abundant trophic group, with a proportion in the community near 66% at the most contaminated site, K1. Bacterivores were the second most common group, representing more than 50% of the total nematode populations at K2 and K3. This group was positively correlated with Corg and pH (P<0.01) (Table 5). Fungivores, considered relatively insensitive to disturbances, including heavy metal pollution, occurred in relatively low densities, except at K2 with 8.98% of the total population. Omnivores and predators were most affected by the pollutants, with very low densities at K1-K3. The low resistance of these two groups to disturbances is in agreement with their negative correlation (P<0.01) with Cr (predators) or with all heavy metals (omnivores). Both trophic groups were also negatively correlated with Ninorg., and soil moisture (Table 5). The distribution of the c-p groups near the plant was consistent with their life strategies and survival abilities. General opportunistic nematodes, c-p 2, were most common at the most polluted sites (K1-K3), followed by c-p 1. The other three c-p groups represented only ca. 10% of the identified nematodes. The numbers of c-p 4 and 5 nematodes were significantly higher at the most remote site, K4, where representatives of c-p 4 were the most abundant within the nematode community (Table 4).
ECOLOGICAL INDICES
Mean H′ and generic richness were highest at K4, indicating the richest composition of nematode taxa (Table 4). MI2-5 and SI, measures of ecosystemic maturity, showed analogous development (Figure 2), with stable values from K1 towards K3 and steep increases at K4 (Table 4). EI values indicated that K2 stored the highest amounts of organic matter available for degradation, but K1 had the highest rate of degradation, as indicated by the lowest CI value (P<0.05) (Table 4).
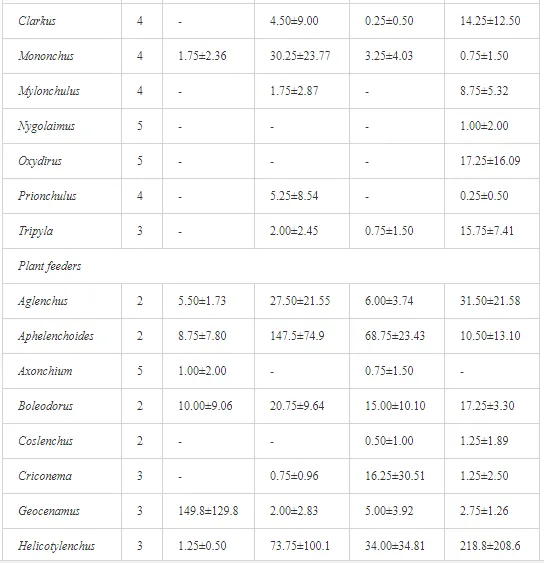
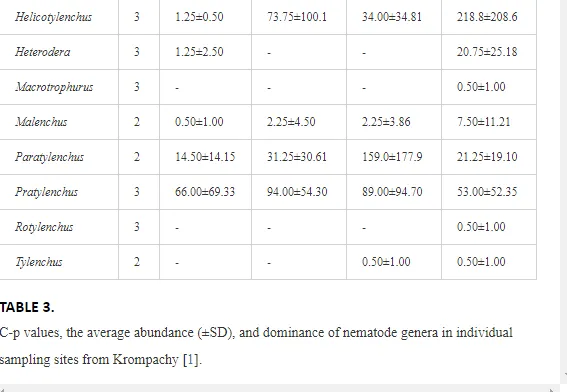
Several significant relationships between the heavy metal contents in the soil and the ecological indices were observed across all sampled sites (Table 5). As an indicator of diversity, generic richness was negatively correlated (P<0.05 or <0.01), with nearly all heavy metals except Ni, similar to H′ (except Ni and Pb). SI and MI2-5 were negatively correlated (P<0.01) with Cr content
DISCUSSION
Heavy metals can both directly and indirectly affect soil environments, directly by modulating the physiology and behaviour of the soil fauna and flora, or indirectly by altering environmental conditions such as pH or resource availability [27, 28]. The solubility of heavy metals in soil, for which substrate pH is the main driver, determines their toxicity to soil biota [3]. The soil conditions (mostly pH) in the Krompachy area suggest that the solubility of heavy metals could be relatively low, but only the solubilities of As and Cr were low. The solubility and thus the accessibility of the other heavy metals with >20% potential mobility at all sites (K1-K4) could be considered a consequence of chronic contamination of the soil profile and/or a low ability of the soil to bind these elements. The values of the soil parameters and the trend of heavy metal contamination along the transect ruled out the impact of natural geological and/or physicochemical properties. Kovohuty JSC Krompachy was thus the most likely source of the higher heavy metal levels. This conclusion is in agreement with previous data collected from this area [17, 29, 30]. The influence of polymetallic pollution is evident in all aspects of soil ecosystems, including communities of soil nematodes and their trophic structures. Bacterivores and plant feeders were the most resistant to the adverse effects of pollution, consistent with the findings of a previous study in this area [31]. On the other hand, acidic soil combined with heavy metal pollution can positively influence mostly fungi and decrease bacterial densities [32, 33], but our results do not support these effects. We found relatively low proportions of fungivores and high proportions of bacterivores in the acidic soils at most sites. Numerous studies [34, 35, 36, 37] have described differences in the survival of soil nematodes with similar ecological and life strategies under harsh abiotic circumstances, including heavy metal contamination. Fungivores, such as representatives of the genus Aphelenchus tolerant to contamination [38, 39], should thus be more abundant under such environmental contamination. The density of Aphelenchus, however, was significantly higher only at K2, which could indicate that interacting environmental factors (e.g. moisture and texture) might have an important impact on the population density of this trophic group [40].
Omnivores and predators are generally considered the most sensitive to any disturbances and stresses [41, 42, 43]. Our data supported the high sensitivity of these two trophic groups and their preference for more eco-friendly conditions over polluted environments. In addition, only these two groups were strongly negatively correlated (P<0.01) with heavy metal pollution. Specifically, omnivores correlated negatively with all heavy metals (P<0.01), and predators strongly correlated negatively (P<0.01) with Cr. Nagy et al. [44] reported similar findings from a field experiment in Hungary, where the lowest concentration of the Cr mobile fraction that produced an observable effect was approximately 0.5 mg kg-1. The presence of the more toxic and mobile Cr6+, which our assay could not detect, may have been responsible for the significant influence of Cr on these two trophic groups, despite the lower Cr concentrations in our study. A synergistic contribution of other heavy metals may also have been responsible for the stress response of these trophic groups.
Community characteristics and ecological indices (H′, MI2-5, and SI) indicated that the soil conditions at our sites were significantly stressed by the contaminants. Generic richness and H′ were lower under higher loads of heavy metals. The lightly contaminated K4 site had the highest diversity of nematode genera, belonging to the entire c-p scale, including opportunists (e.g. Rhabditis, Acrobeloides, and Aphelenchus) and persisters (e.g. Dorylaimus, Oxydirus, and Nygolaimus). The proportion of persisters with higher c-p values rapidly decreased with increasing pollution, which consequently led to lower nematode diversity and a simplification of the food chain. Diversity was mostly negatively correlated with the degree of pollution, but nematode abundance increased at moderately contaminated K2 and K3, but rapidly decreased under a heavy load at K1. Sánchez-Moreno et al. [39] reported similar findings in southern Spain after the Aznalcollar mining spill. A higher generic diversity reflects a higher resilience of ecosystems and complexity of relationships at all trophic levels [45, 46]. A decrease in generic diversity may cause an ecosystem to regress to an earlier successional stage or even to collapse. On the other hand, an increase in total density under a low or moderate degree of pollution does not necessarily indicate an uncontaminated environment but rather better survival conditions, as in our study (the growth in the population of opportunistic nematodes). Contamination can in some cases act as a direct or indirect stimulus to a particular component of the ecosystem and lead to inaccurate assessments of the actual environmental state [4]. Nevertheless, the generic composition of the nematode communities and several of the ecological indices (EI, SI, and MI2-5) suggest that a certain amount of regression is occurring in the study area closer to the pollution source.
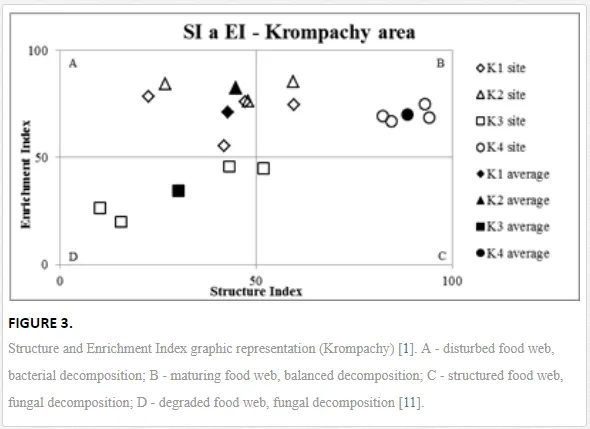
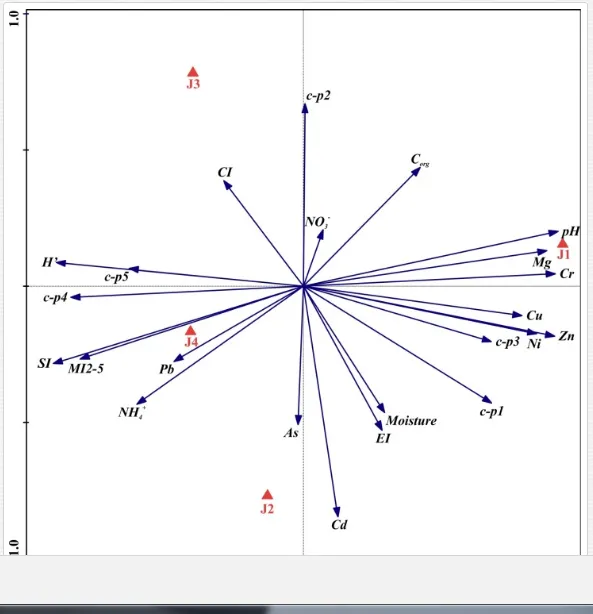
Georgieva et al. [42] have studied the combined effect of heavy metals. The maturity of an ecosystem, measured by MI2-5, was negatively affected more under significantly lower polymetallic contamination than if the heavy metals were applied separately. A nematode community was highly insensitive to Cd, showing no significant changes, at soil concentrations up to 160 mg kg-1 [47]. Similar insensitivities in nematode communities were also described for increased levels of As [48]. The toxicity of some elements, though, can increase in combination with other heavy metals and may have negative impacts on nematodes [42]. This synergistic effect could thus be responsible for the decrease in MI2-5 and SI towards the pollution source in our study, despite their nonsignificant correlation with the heavy metals. The analysis of SI and EI at Krompachy indicated significant differences amongst the sites in structural complexity and resource availability of the ecosystem. The graphic representation of the SI and EI parameters (Figure 3) mapped K4 in quadrat B (maturing ecosystem with low or moderate disturbance), K1 and K2 in quadrat A (ecosystem under high disturbance and with a disturbed food web), and K3 in quadrat D (stressed ecosystem with a degraded food web). These results indicated differences in the composition of the structural component (c-p groups 3-5) rather than the enrichment component (c-p 1) [49]. The shift in the ecosystem in our study under heavy metal pollution corresponded well with the conditions reported by [50, 51, 52].
The decomposition of organic matter can also have a large impact on the development of a soil ecosystem and its maturity. The rate of breakdown of organic matter depends on soil conditions and the participation of a variety of decomposers [11]. We studied decomposition using CI and found that the breakdown of organic matter followed distinct degradation pathways at the different sites. EI indicated high levels of energy resources at all sites except K3, but CI indicated that the quality of these resources (C:N ratio) differed: K1 and K3 had mainly bacterial pathways of degradation, dominant in N-enriched conditions, but the other sites had a slower breakdown, with an increasing importance of fungi breaking down organic matter with a higher C:N ratio. The change from fast to slow decomposition was also apparent in the nematode community structure and the substitution of bacterial enrichment opportunists (mainly Rhabditis) by more efficient general opportunists (Cephalobus and Acrobeloides).
Indirect effects of industrial emissions – A case study of SMZ JSC Jelšava
RESULTS
HEAVY METALS
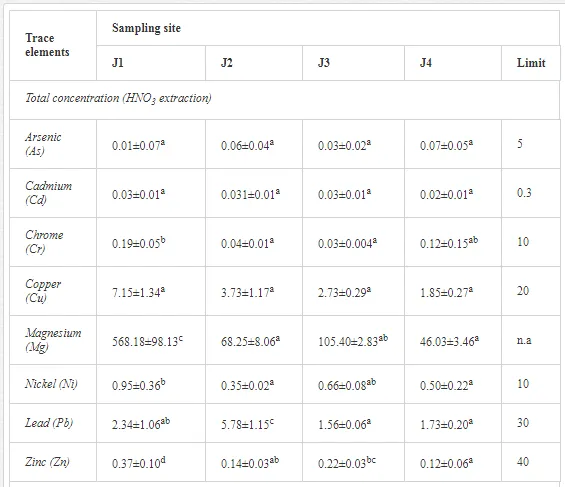
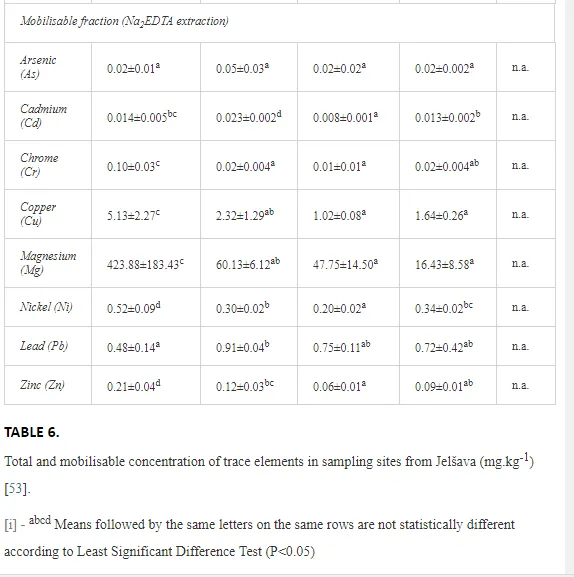
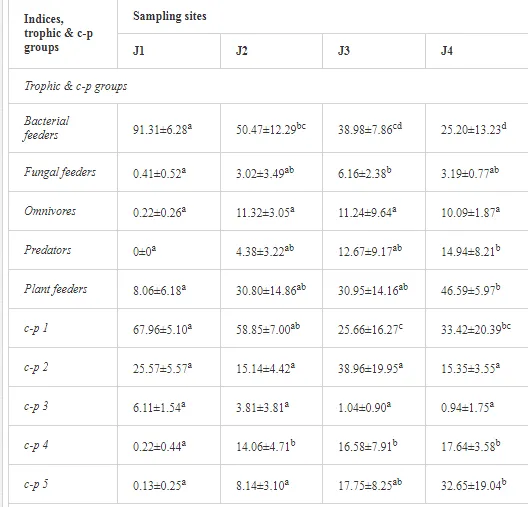
The total concentrations of heavy metals in the soil were relatively low and did not exceed the limits for uncontaminated soils (Table 6) set by [26]. Only the concentration of Mg increased, where the total and mobilisable concentrations were more than ten-fold higher at J1 (568.2 and 423.9 mg kg-1, respectively) than at J4 (46.03 and 16.4 mg kg-1, respectively). The increasing Mg gradient, but also for other heavy metals (Cr, Cu, Ni, and Zn) towards the pollution source (J1) is shown in Figure 4.
COMPOSITION OF THE NEMATODE FAUNA: TROPHIC AND C-P GROUPS
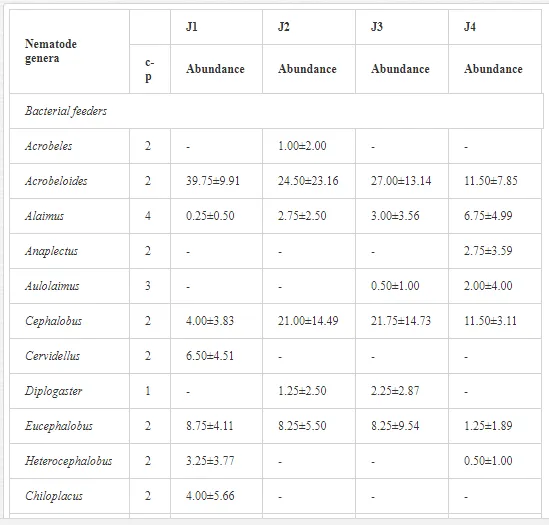
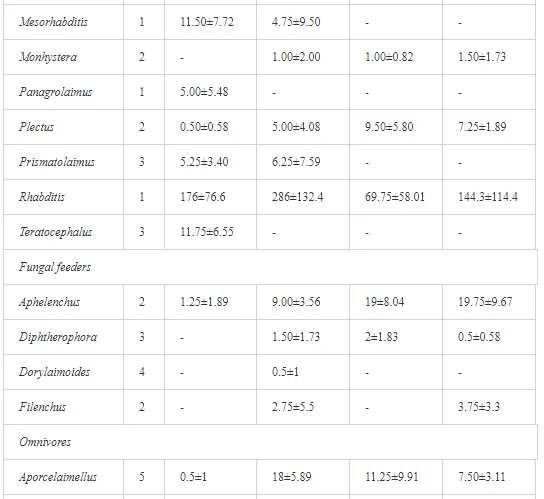
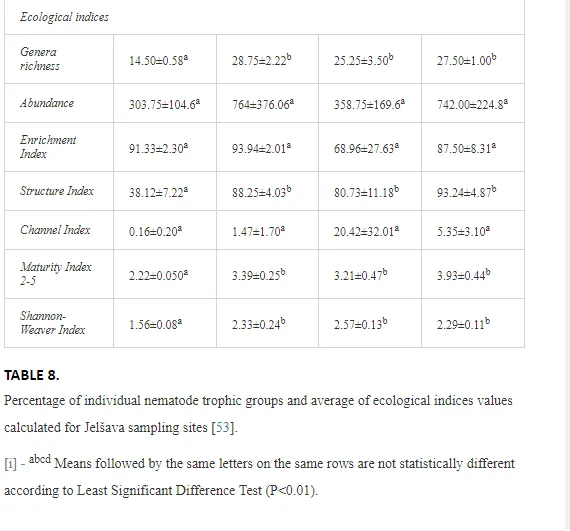
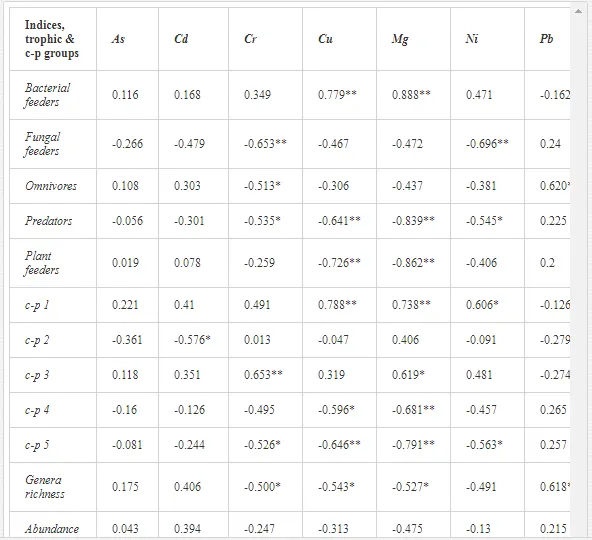
A total of 52 nematode genera were identified (Table 7). The abundance of most genera, e.g. Helicotylenchus, Aphelenchoides, Axonchium, and Oxydirus, increased with distance from the pollution source, but some genera, e.g. Acrobeloides and Rhabditis, dominated only at the most polluted site, J1. The generic richness was approximately two-fold higher at J2-J4 than at J1 (Table 8) and, as with abundance, was significantly (P<0.01) limited by pH (Table 9).


The soil pH and concentrations of Mg, Cr, Cu, Ni, and Zn strongly (P<0.01) influenced all trophic groups, predators and omnivores in particular (Tables 8 and 9). Bacterivores, with more than 90% proportion in community at J1, were the only trophic group with a positive correlation (P<0.01) with pH, Cu, Mg, and Zn (Table 9). The proportion of plant feeders, the second most abundant trophic group, was relatively low (8.1%) near the pollution source, while fungivores reached a proportion of only 0.41%, omnivores 0.22%, and predators were absent in community (Table 8). The distribution of the c-p groups amongst the sites supported their mapping according to r/K characteristics. The group most tolerant to pollution, c-p 1, dominated under strong contamination (Table 8) and was able to survive even at the higher concentrations of Mg, Zn, and Cu (Table 9). The abundance of c-p 3 was positively correlated only with Cr and Zn (Table 9) and was highest at J1 (Figure 4), mostly due to a high frequency of bacterivores (Prismatolaimus and Teratocephalus) and plant feeders (Pratylenchus) (Table 7). In contrast, c-p 4 and 5 were sensitive to Cu, Mg, and Zn contamination and alkaline soil (Table 9), and occurred predominantly at the sites farthest from the pollution source. Representatives of c-p 2 were positively influenced mainly by Corg.
ECOLOGICAL INDICES
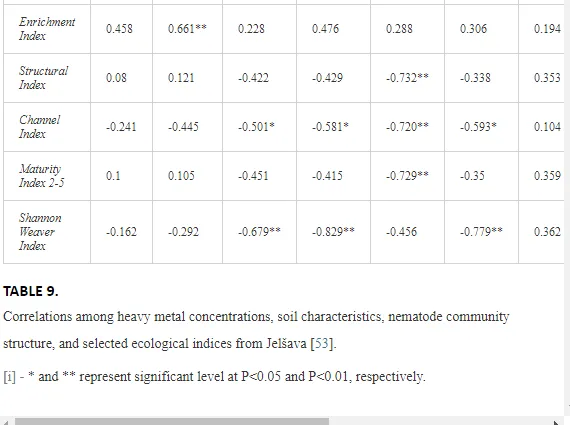
The ecological indices indicated degradation of the soil ecosystem at J1, most likely due to the exceptionally high alkalinity and Mg content (Figure 4). J3 had the highest diversity, as shown by H′, which decreased towards J1 (Table 8). MI2-5 and SI supported this trend, with significant changes (P<0.01) in values between J1 and J2 (Table 8). The amount of available food resources in the soil system identified by EI was similar at all sites, but J3 had slightly less favourable conditions (Table 8). A graphic representation of EI and SI suggested a higher level of ecological disruption at J1 relative to the other sites (Figure 5). The trend in CI values reflected the increasing importance of fungi in the decomposition of organic matter with distance from the pollution source. The high concentration of Mg; higher levels of Cu, Zn, and Corg; and soil alkalinity were the most important factors influencing the structure and maturity of the nematode communities (Table 9, Figure 4).
DISCUSSION
In this case study, the long-term industrial emission of magnesite has affected the soil ecosystem, mostly by changing the basic soil conditions. Such high loads of Mg in the soils as recorded in our study are rare, so the impact of Mg emissions on soil fauna is not often studied and is not yet understood [53]. Similar steep increases in soil alkalinity as a direct consequence of industrial inputs of Mg as was found in our assay described also Machín and Navas [54]. Most studies have investigated the importance of Mg deficiency in higher plants as a trace element important in photosynthesis. Hronec [17] described a decrease in soil fertility and the replacement of native plant species by tolerant halophytes in an area with high Mg input. Moreover, the long-term fallout of Mg dust (>600 t km-2 y-1) may degrade natural ecosystems and create corrosive crusts that could affect natural interactions in the soil even more [17]. The absence of sensitive nematode groups, likely caused by an ineffective regulation of osmotic pressure by their cuticles due to changes in the concentrations of various ions in the soil pore water, can be a direct effect of altered soil conditions [55]. The concentrations of ions in soil solutions under extreme changes in pH may negatively affect the regulation of water by organisms [56], thereby disrupting homeostasis. A change in the concentrations of soil ions may thus have been an important factor responsible for the decrease in the higher c-p groups (mainly predators and omnivores with highly permeable cuticles) at the sites with high pH and Mg concentration. The indirect influence of contamination was likely a restriction in the availability of resources and the interactions necessary for survival or an effect on the abiotic attributes of the environment [32].
In areas with neutral soil pHs (as at J4), strong shifts in soil composition are usually expected after an increase in pH. Alterations in edaphic diversity after pH manipulation have been confirmed experimentally and by field studies. Earthworms, enchytraeids, and nematodes were more abundant after liming [57, 58], but Acari preferred acidic conditions [59, 60]. The altered soil conditions in our study as a consequence of Mg contamination and an extremely high pH have led to direct and indirect effects on the nematode communities and most likely influenced the composition of the entire soil fauna. The plant feeders showed the first signs of the indirect effects of high Mg levels. A fluctuation in plant feeder density is generally considered a sign of changes in primary production [61]. Excessive concentrations of Mg under alkaline conditions induce a deficiency of essential nutrients (e.g. Ca and P) and impede the development of plant root systems [62]. Relatively impoverished phytocoenoses composed mainly of halophytes such as Puccinellia distans or Agrostis stolonifera are usually found near pollution sources [63]. A shift towards bacterivorous nematodes in the community was another indication of an indirect influence of pollution in our study, because bacteria prosper more than fungi at alkaline pHs [63].
An abundance of food for bacteria often increases the proportion of c-p 1 bacterivores, as confirmed experimentally by [58]. Representatives of the genus Rhabditis were the most abundant nematodes along the entire transect in our study. The survival and dominance of Rhabditis and other bacterivores in this hostile environment could, however, be a complex phenomenon, comprising not only food resources, but also behavioural and physiological adaptations to the hostile conditions [64]. For example, C. elegans can withstand high pH and salinity and survive under extreme osmotic pressure [55, 65]. Moreover, c-p 1 nematodes can produce inactive dauer larvae, which increase the chances of withstanding harmful or limited conditions. Other studies [1, 4] have shown that c-p 2 nematodes are also able to withstand severe ecological conditions and comprise the dominant c-p group in highly disturbed ecosystems [66]. Our results only partially supported these findings. More than 25% of the nematodes at J1 belonged to the c-p 2 group, and of these, species of Cervidellus and Chiloplacus were the most tolerant. The proportion of c-p 2 nematodes within the community, however, was significantly lower than that of c-p 1 nematodes. The discrepancy between the hypothetical dominance of stress-tolerant c-p 2 nematodes and our results was likely due to various physiological and ecological aspects of c-p 1 and 2 nematodes and their population dynamics (e.g. reproduction rate, length of life cycle, and resource availability). The abundance of c-p 1 nematodes in the soil may also be due to, aside from soil fertility reported by [11], the changes in soil pH. Further study is necessary to confirm these possibilities
. 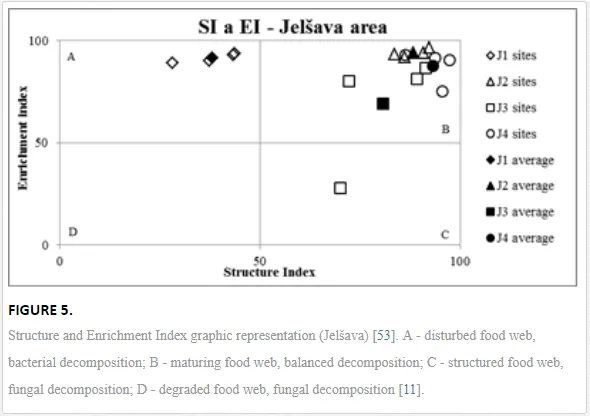
This study has demonstrated the negative ecological impact of contamination by quantifying different ecological indices (e.g. SI, MI2-5, and H′) and measuring key parameters of nematode communities (generic richness and abundance). Not all communities traits showed a clear response to stress in the ecosystem, and some responded inconsistently, e.g. abundance similar as in the Krompachy case study did not reflect the stress of the ecosystem. Total abundance should thus not be used as an indicator for either heavy metals, as suggested by [42], or physical or chemical changes in soil properties such as pH. Generic richness and H′, though, indicated substantial differences in species diversity in the ecosystems with diverse contamination and soil salinity, in accordance with diversity shifts observed in other nematode communities [58] and in other edaphic groups after pH manipulation [59, 67]. SI and MI2-5 were the best tools in our study for showing the impact of high Mg concentrations and soil salinity on nematode community structure and the maturity of the ecosystem. SI combined with EI identified J1 as severely disturbed (quadrat A), and the other sites showed only a low degree of stress. A decrease in the intensity of stress and an increase in the complexity of soil community structure with distance from a pollution source have been reported in several other areas of intensive industry [1, 44]. Based on low CI values in our study, indicating predominant bacterial pathway of decomposition, c-p 1 enrichment opportunists were eliminated from maturity assessment (MI2-5), as they respond more to the food availability than pollution [47]. Eliminating the influence of enriched conditions provided us with clear gradual increase in environment stability and maturity from the site J1 onwards.
Conclusions
Heavy metal contamination of soil is long-term ecological problem. High levels of pollutants may lead to losses in production, breaches in the otherwise strict sanitary limits for agricultural products, and health-related problems for local inhabitants. This study demonstrated that the background geochemical heavy metal content was significantly exceeded, with measurable consequences for the local environments. The sensitive groups of soil nematodes, mainly omnivorous and predacious nematodes of the higher c-p groups, were significantly suppressed in the ecosystems, and tolerant groups, with better physiological and behavioural adaptations to harsh conditions, survived. Such alterations in community structure may have far-reaching consequences, because some of the ecological regulation or environmental feedbacks provided by nematodes may be suppressed in, or eliminated from, the ecosystem. Despite the recent decrease in emissions and the application of various treatments to prevent their leakage at both metallurgical plants, the potential threat of further environmental deterioration remains relatively high. The high concentrations of possible toxic elements bound to the soil matrix and temporally unavailable to the soil biota are the main threat in the Krompachy area. The release of the pollutants to the soil solution by sudden shifts in local soil conditions, e.g. an increase in soil acidity by acid rain, could lead to their increased toxicity to soil communities or to groundwater contamination. The threat from pollution to the ecosystem around Jelšava is less imminent, because the levels of toxic elements were not significantly higher. The high Mg concentrations and soil salinity, and consequently the extreme soil alkalinity, however, are the most important problems in this area. Under these conditions, only a few organisms with adaptations for surviving in such an environment are able to prosper, as our results clearly showed. In both case studies, the nematode community structures collapsed near the pollution sources, with the domination of nematodes able to survive inhospitable soil conditions.