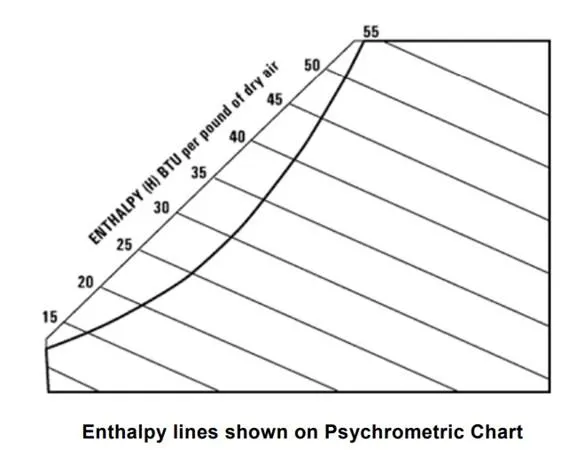
A force exerted on a body can cause a change in either the shape or the motion of the body. The unit of force in SI system is the newton (N) and CGS system is dyne. No solid body is perfectly rigid and when forces are applied to it, changes in dimensions occur. Such changes are not always perceptible to the human eye since they are negligible. For example, the span of a bridge will sag under the weight of a vehicle and a spanner will bend slightly when tightening a nut. It is important for civil engineers and designers to appreciate the effects of forces on materials, together with their mechanical properties of materials.
There are three main types of mechanical forces that can act on a body. They are:
1. Tensile force
2. Compressive force and
3. Shear force
Tensile force that tends to stretch a material, as shown in the figure 1 below.
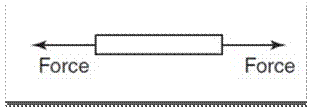
Figure 1: Tensile force
For example,
1. Rubber bands, when stretched, are in tension.
2. The rope or cable of a crane carrying a load is in tension.
3. When a nut is tightened, a bolt is under tension.
A tensile force will increases the length of the material on which it acts.
2. Compressive force
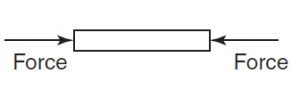
Compressive force that tends to squeeze or crush a material, as shown in the figure below.
For example,
A pillar supporting a bridge is in compression.
- The sole of a shoe is in compression.
- The jib of a crane is in compression.
- A compressive force will decrease the length of the material on which it acts.
3. Shear force
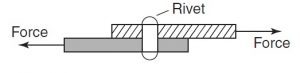
Shear force that tends to slide one face of the material over an adjacent face.
For example,
- A rivet holding two plates together is in shear if a tensile force is applied between the plates as shown in Figure
- A guillotine cutting sheet metal, or garden shears, each provide a shear force.
- A horizontal beam is subject to shear force.
- Transmission joints on cars are subject to shear forces.
A shear force can cause a material to bend, slide or twist.