ALGAE AS AN ALTERNATIVE FUEL FOR DIESEL

In view of
the depleting oil reserves and exponential rise in petroleum prices, the search
for alternative sources of fuel is very timely and important. The present paper
addresses the underlying issues in biodiesel production from biomaterials and
sustainable production and supply of first-generation biofuels, especially the
one from jatropha. The agencies and research institutions involved in
the production of biofuels and the national and international efforts made in
this regard are discussed here. There is also a dire need of a step towards
large-scale production and supply of second-generation biofuels,
although in
infant stage, to strengthen the world economy in general and Indian economy in
particular. However, the production of biofuels are likely to have serious
socio-economic implications especially to the lesser developed societies. This
needs serious attention from policy makers and public at large.
TYPES OF ALGAE

TYPES OF ALGAE

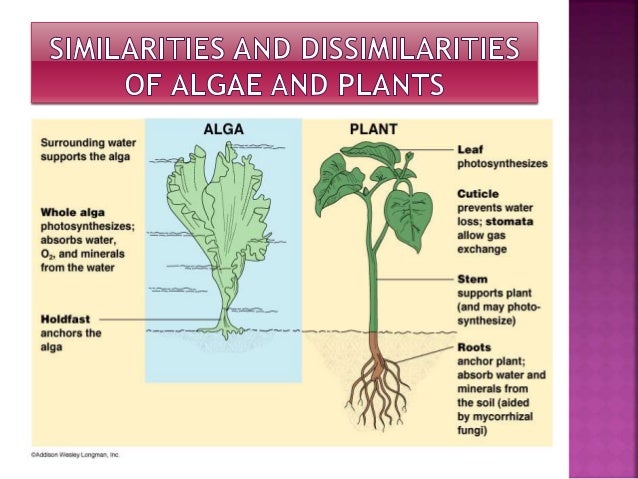
ABOUT ALGAE:
The
word algae represent a large group of different organisms from different
phylogenetic groups, representing many taxonomic divisions. In general algae
can be referred to as plant-like organisms that are usually photosynthetic and
aquatic, but do not have true roots, stems, leaves, vascular tissue and have
simple reproductive structures. They are distributed worldwide in the sea, in
freshwater and in wastewater. Most are microscopic, but some are quite large,
e.g. some marine seaweeds that can exceed 50 m in length.
The unicellular forms are known as microalgae where
as the multicellular forms comprise macroalgae.

›Algae Biodiesel is a good replacement for standard crop Biodiesels like soy acanola›Up to 70% of algae biomass is usable oils›Algae does not compete for land and space with other agricultural crops›Algae can survive in water of high salt content and use water that was previously deemed unusable





